Ppeer-reviewed studies demonstrate that worthwhile frontline jobs make more satisfied, engaged, and productive workers who contribute directly to greater business profitability and above-market investment returns.
Yet, business leaders lack the tools that would enable them to understand how the behaviors, attitudes, and interactions within their own organizations contribute to these desired worker and business performance outcomes, or to calculate the impact of improving working conditions so they can identify the strategies most likely to be successful.
The goal of this project is to develop a computer simulation that quantifies the link between elevating the workplace experience of frontline workers and superior business results.
Researchers
Paolo Gaudiano

Paolo Gaudiano is president of Aleria Research Corporation (ARC), chief scientist of Aleria (a human-centered technology company that measures inclusion in the workplace), adjunct associate professor at the NYU Stern School of Business, and chairman of the annual Diversity & Inclusion Research Conference.
These activities combine Paolo’s decades of experience in business, technology, and academia to transform how people think about diversity and what they do about it, with the ultimate goal of making our society more inclusive and equitable.
Paolo is a Forbes contributor on diversity and inclusion, has written for and been interviewed by several other media outlets, and is a sought-after public speaker—having given hundreds of presentations in the U.S. and abroad, including a TED talk.
He holds degrees in applied mathematics, aerospace engineering, and computational neuroscience, and is the recipient of numerous awards including a Moonshot House Fellowship from the Kravis Center for Social Impact (2019), a Young Investigator Award from the Office of Naval Research (1996), and a Neuroscience Fellowship from the Sloan Foundation (1992). He was a tenured faculty member at Boston University, and he taught at Tufts University and CUNY before joining NYU.
Chibin Zhang

JWith a Master’s in Finance from University of Melbourne (Australia) and a Master’s in Economics from CUNY in New York City, Chibin started her career as a Research Associate at Aleria. She aims to leverage her expertise in finance, economics, and quantitative analysis to address the issue of inequality in our society. More specifically, she is trying to quantify the impact of diversity and inclusion in corporations by designing agent-based simulation models. Her goal is to use the results of her simulation to promote diversity and inclusion in workplace, entrepreneurship, and academia.
Chibin’s previous projects have been funded by the National Science Foundation and Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation.
IRC® + IRC4HR® Project Publications and Learning Materials
J-QIE demo video
Project Details
A search of the literature reveals thousands of peer-reviewed studies that demonstrate that worthwhile frontline jobs make more satisfied, engaged, and productive workers who contribute directly to greater business profitability and above-market investment returns.
Yet, business leaders lack the tools that would enable them to understand how the behaviors, attitudes, and interactions within their own organizations contribute to these desired worker and business performance outcomes, or to calculate the impact of improving working conditions so they can identify the strategies most likely to be successful.
This project bridges the gap between research and business application by creating a simulation tool that quantifies the impact of improving job quality for frontline employees. By linking job-quality initiatives to measurable business outcomes like profitability and employee performance, the Job-Quality Impact Explorer (J-QIE, pronounced “Jackie”) provides a powerful, evidence-based framework for organizations to design better workplaces—proving that enhancing employee wellbeing isn’t just ethical; it’s also smart business.
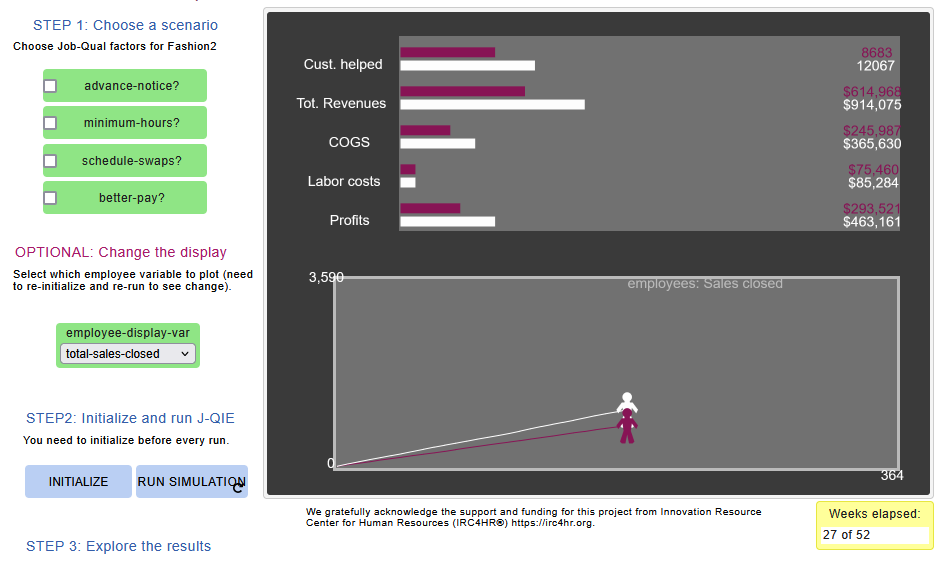
J-QIE combines cutting-edge simulation technology with evidence-based insights to explore how changes to job quality influence frontline worker satisfaction and organizational success. Developed as an agent-based simulation using NetLogo (a free, programmable modeling environment that is used to build models, analyze data, and explore complex systems), J-QIE models two organizations with identical setups, differing only in the implementation of four job-quality initiatives: advance notice of scheduling, guaranteed minimum hours, schedule-swapping flexibility, and improved pay.
Through dynamic simulations, J-QIE demonstrates causal links between job quality factors and key performance indicators such as absenteeism, task efficiency, sales outcomes, and profitability. For instance, in simulations where all job-quality factors are implemented, businesses showed improved revenue and higher profits compared to counterparts with fewer initiatives applied.
Using a selection of research-based job quality models and frameworks, the simulation encompasses key performance indicators (KPIs) and job characteristics, which yields two dramatic benefits. First, rather than relying on correlations from past data to estimate the likely impact of various initiatives, the simulation clarifies and quantifies the causal relationships that connect job characteristics and corporate outcomes. Second, because the simulation captures causal relationships and simulates the day-to-day activities unfolding over time, it functions as a predictive tool for quantifying the impact of various what-if scenarios for each organization that uses it.
J-QIE is not just a simulation—it’s a visionary step toward equipping organizations with actionable insights to create better workplaces, proving that what’s good for employees can also be great for business.
Deliverables
Key deliverables of this project included a downloadable desktop version of J-QIE, a web-based HTML version, and comprehensive documentation to guide users.
The application supports the near-term goals of education and research on the use of agent-based simulation, while demonstrating the ability to quantify the impact of changing job characteristics under a set of representative scenarios. In the long term, the simulation serves multiple purposes: (1) it serves as an explanatory tool to demonstrate in a visually compelling, intuitive fashion, the causal relationships between job characteristics and overall organizational performance; (2) it provides a quantitative assessment of the impact of job conditions and the KPIs specific to each company; (3) it allows each organization to estimate the beneficial impact of improving specific working conditions and to identify the strategies most likely to be successful.
Additionally, the Aleria Research Corporation (ARC) team created an introductory video and a dedicated webpage hosted on ARC’s website, showcasing J-QIE’s potential to predict the outcomes of workplace interventions.